O-Ring NSF
Get a Quote

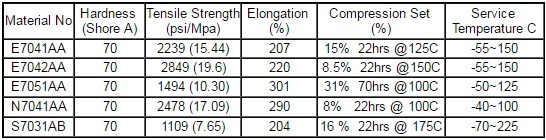
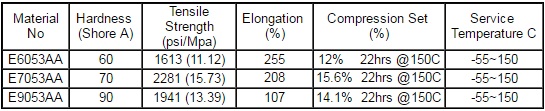
O-Ring NSF Certified
GMORS offers o-rings and seals for drinking water applications with
compliance to WRAS Standards and NSF 61 (National Sanitation Foundation).
Our R&D team of engineers formulate at least 20 compounds suitable for
drinking water applications complying with the above standards.
NSF Standards 61: The guidelines which regulate the requirements of
system components and chemicals that is exposed to drinking water during
treatment is NSF Standards 61. The standards ensure that chemicals and
substances that are toxic do not end up in drinking water systems, causing
adverse effects on health.
WRAS: Water Regulations Advisory Scheme
The approval scheme in the United Kingdom that regulates the use of
components and materials to ensure non-contamination of water supply system
sis the WRAS.
Background
For many years, the potable water industry makes use of chlorine as a
disinfectant against bacteria. However, the use of chlorine in drinking
water systems gives rise to DBP (disinfectant-by-products) which at higher
concentration, has been shown to be carcinogenic. The EPA (Environment
Protection Agency) set limits on the level of disinfectant-by-product to be
found in potable drinking systems.
The new regulatory limits set by the Environment Protection Agency resulted
in chloramine been used as a substitute for chlorine as municipalities,
water processing and distribution facilities find ways to reduce
disinfectant-by-products caused by chlorine usage. Although chloramine
produces less DBP, it has a damaging effect on elastomeric seals, giving
rise to a loss of resilience and excessive swelling. A higher incidence of
failure of elastomeric seals and gaskets occurs with the use of chloramine
as disinfectant, with sulfur-cured elastomers performing less satisfactory
than peroxide-cured elastomers. It has been tested and shown that chloramine
has a more damaging effect on certain elastomers.
GMORS Solution: Chloramine-Resistant Elastomers
Sealing systems formulated to be chloramine resistant are offered by GMORS,
with a selection of elastomeric compounds available.
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) has excellent resistance to
chlorine found in drinking water, and is extensively used in drinking water
systems. At higher concentrations of chlorine or chloramine however,
additional resistance testing is necessary. Formulation-resistant
formulations of EPDM has a higher level of saturated ethylene and a lower
level of carbon black.
Silicone (VMQ) performs better against chloramine attack as compared
to other elastomers. However, silicone has a lower abrasion resistance and
lower tensile and tear strength. The lesser mechanical properties of
silicone has to be taken into account while considering the benefits of its
resistance to chloramine attack.
Contact us for a cost efficient recommendation of a chloramine-resistant
sealing system.
Copyright © 2017 Ge Mao Rubber Industrial Co., Ltd.